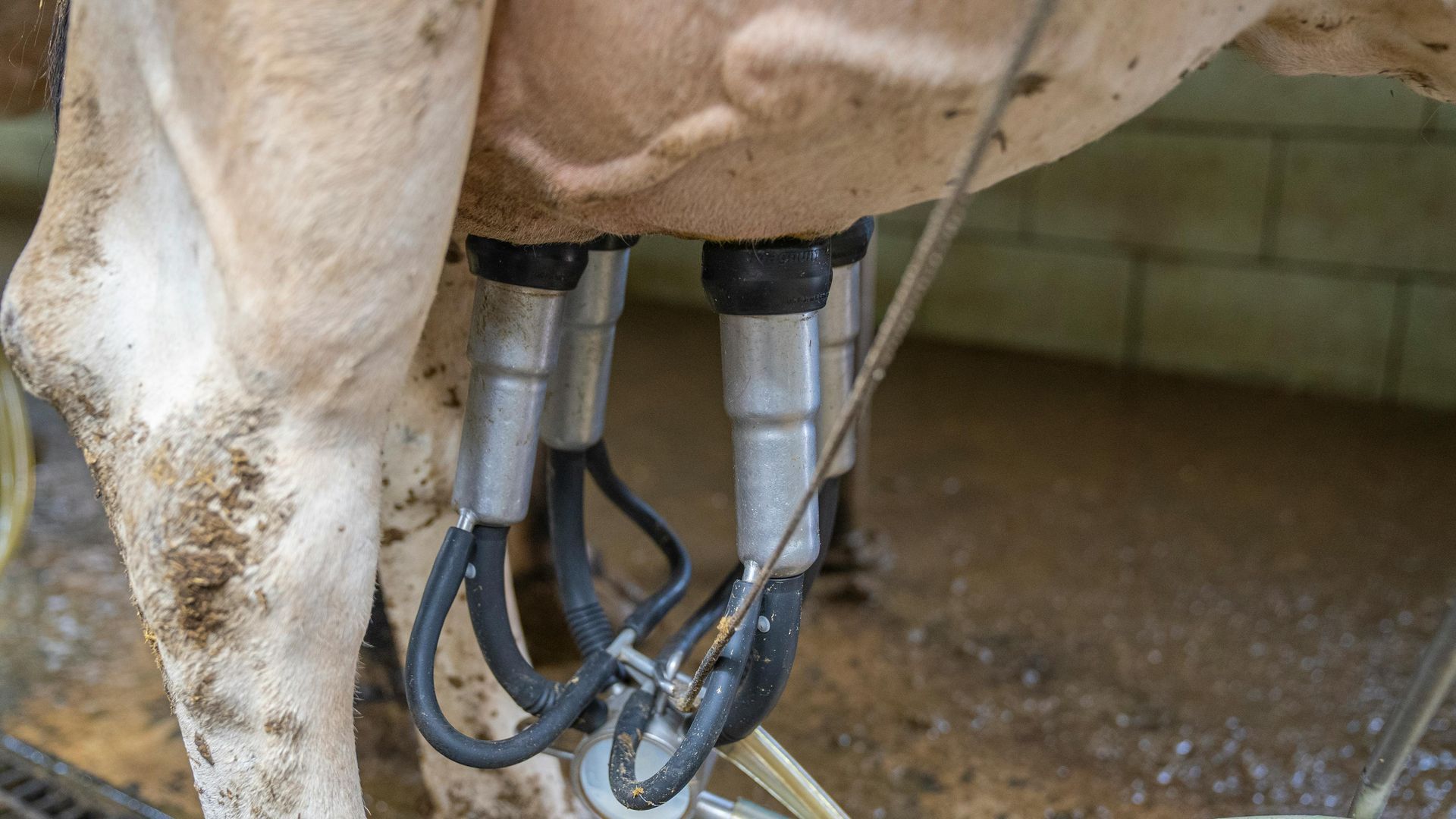
Introduction to Robotic Milking for Virginia Dairy Farms
As Virginia's dairy industry evolves, the integration of automation is reshaping how farmers manage their operations. One of the most transformative advancements in this space is robotic milking. Also known as automatic milking systems (AMS), these technologies allow cows to be milked without direct human intervention, offering potential benefits in labor savings, animal welfare, and overall efficiency.
Virginia dairy farms, ranging from small family-owned operations to larger commercial enterprises, are exploring robotic milking as a strategic investment in the future of sustainable farming. For many, learning about available services that support the adoption of advanced equipment is an important step in making automation work for their operations. At the same time, understanding the history and mission behind trusted agricultural suppliers—like those shared on their About Us page—helps farmers choose partners who can guide them through the transition.
Key Takeaways
- Robotic milking systems (RMS) automate the cow-milking process using sensors and robotics.
- Virginia’s dairy farms are considering RMS to address labor shortages and improve efficiency.
- These systems track individual cow data, offering insights for herd health and milk quality.
- Installation and maintenance costs can be high, requiring thoughtful planning and investment.
- Transitioning to robotic milking involves changes in barn layout, herd management, and workflow.
- Long-term benefits may include increased productivity, better cow health, and improved work-life balance for farmers.
What is Robotic Milking?
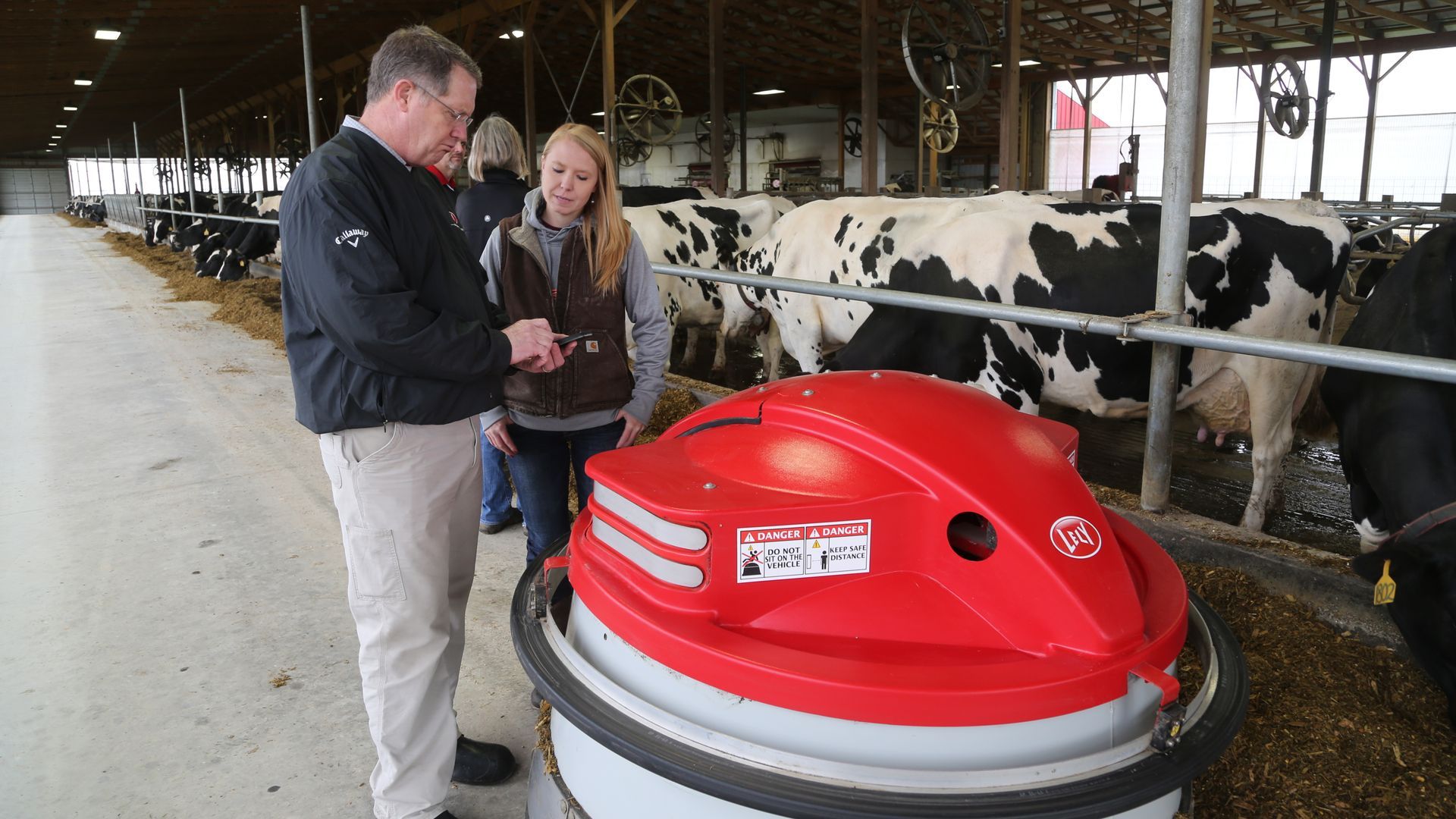
Robotic milking is a technology-driven solution that allows cows to be milked automatically, usually whenever they choose to enter the milking unit. This system uses robotic arms, sensors, and computer software to attach milking cups to the cow's teats, collect milk, and analyze data in real-time. The entire process is managed by sophisticated systems that monitor each cow’s health, milk output, and behavior.
These systems have been widely adopted in parts of Europe and are gaining traction in the United States, including in Virginia. As dairy farms face labor challenges and seek efficiencies, robotic milking presents a compelling option. For a deeper look at how technology impacts herd health, see our guide on milking equipment and herd health.
How Does a Robotic Milking System Work?
Robotic milking systems generally include the following components:
- Milking Unit: Equipped with robotic arms and sensors, this unit automatically identifies the cow and attaches the teat cups.
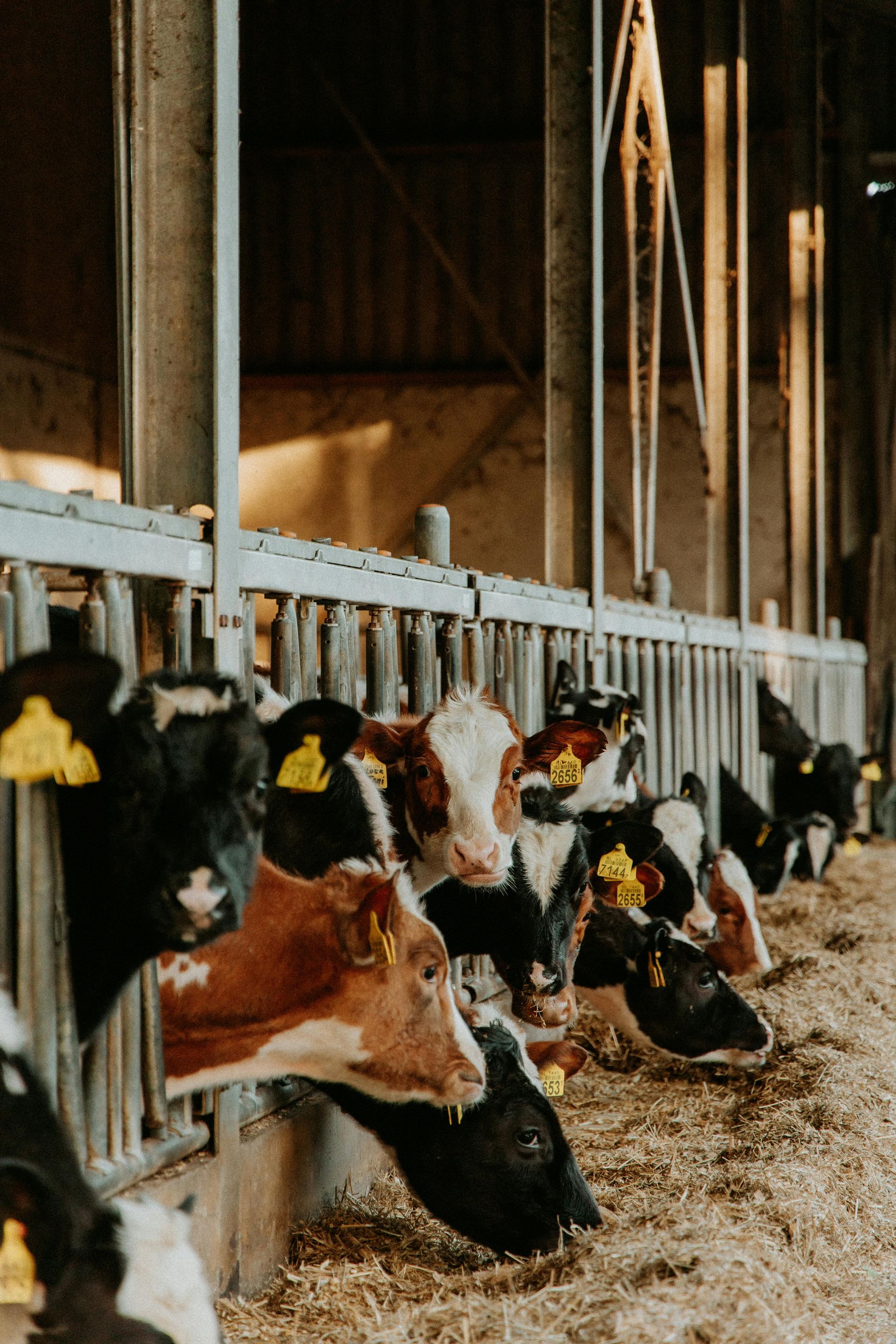
- Cow Identification System: Uses RFID tags or collars to track each cow’s milking history and health metrics.
- Milk Analysis Tools: Measure milk quality, volume, temperature, and conductivity.
- Data Management Software: Collects and analyzes cow-specific data to support management decisions.
- Cleaning Systems: Ensure hygiene by cleaning the equipment between milkings
The process typically works like this:
- A cow voluntarily enters the milking station.
- The system identifies the cow and determines if it is ready to be milked.
- The robotic arm cleans the udder and attaches the milking cups.
- Milk is collected and analyzed in real-time.
- After milking, the cow exits, and the unit is cleaned for the next session.
Farmers interested in a detailed overview may find value in our dairy farmer milking system guide.
Benefits of Robotic Milking for Virginia Dairy Farms
Virginia dairy farmers face specific challenges, such as limited labor availability and high operational costs. Robotic milking can offer several potential advantages:
Labor Efficiency
Automated systems can reduce the need for manual milking labor, which is increasingly hard to find in rural areas. This allows farm workers to focus on higher-value tasks such as animal care and herd management software.
Cow Welfare and Comfort
Robotic systems often allow cows to choose when to be milked, promoting a more natural rhythm. This can reduce stress and improve overall animal health.
Detailed Monitoring and Insights
With real-time data collection, farmers can track milk production, detect early signs of illness, and optimize feeding programs. This can lead to better decision-making and increased productivity.
Improved Work-Life Balance
Farmers benefit from more flexible schedules and reduced physical strain. This can make dairy farming more appealing to the next generation and promote long-term sustainability.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are appealing, transitioning to robotic milking requires careful planning. Some challenges include:
- Initial Cost: Systems can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, not including barn modifications. Learn about milking system upgrade key features that can maximize value.
- Training and Adaptation: Both cows and farm staff need time to adjust to the new system.
- Maintenance: Regular upkeep is necessary to avoid downtime and maintain hygiene.
- Data Overload: Managing and interpreting large volumes of data can be overwhelming without proper training.
Economic Considerations
Investing in robotic milking requires a solid financial plan. Farmers should evaluate the following:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Includes purchase, installation, and infrastructure upgrades. |
| Operating Costs | Covers maintenance, software updates, and electricity. |
| Labor Savings | Reduced need for milking labor may offset some costs. |
| Increased Productivity | Potential for higher milk yields and better herd management. |
| Return on Investment | Long-term payoffs depend on farm size, herd behavior, and system use. |
Transitioning to a Robotic System
Making the shift from conventional to robotic milking is a significant change. Key steps include:
- Planning and Consultation: Work with farm service experts and extension specialists to assess needs and layout changes.
- Infrastructure Updates: Barns may need to be retrofitted or rebuilt to accommodate robotic units. Browse examples in our completed projects.
- Training: Staff and herd need time to adapt. Some cows may resist automation at first.
- Monitoring: Close attention during the initial months is crucial to ensure system success.
If you are considering robotic milking, reach out to us today through our contact page to discuss solutions tailored to your farm.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many cows can one robotic milking unit handle?
Most systems are designed to handle 50 to 70 cows per unit, though this can vary by manufacturer and usage patterns.
Is robotic milking suitable for small farms?
Yes, smaller farms can benefit from automation, especially where labor is limited. Some systems are scalable and designed for smaller herds.
What kind of barn layout works best with RMS?
Free-stall barns with guided cow traffic tend to be most compatible with robotic systems. Modifications may be needed in existing layouts.
How long does it take for cows to adapt to robotic milking?
Adaptation varies. Most cows adjust within a few weeks, especially with consistent training and encouragement.
What are the ongoing maintenance needs?
Systems require regular cleaning, software updates, and occasional technical repairs. Most suppliers offer service contracts for support.
Final Thoughts
Robotic milking represents a significant innovation for Virginia dairy farms, offering the potential to transform how farmers manage their operations. While the transition requires investment and thoughtful change management, the long-term benefits can be substantial. With the right planning, training, and support, Virginia’s dairy farmers can use this technology to improve sustainability, animal welfare, and operational efficiency.
Farmers interested in robotic milking should begin with a thorough assessment of their farm’s layout, herd size, and financial situation. Collaboration with local extension agents, equipment suppliers, and other farmers can help ensure a smooth transition. For guidance on taking the next step, contact us to discuss how robotic milking can work for your farm and receive personalized support.